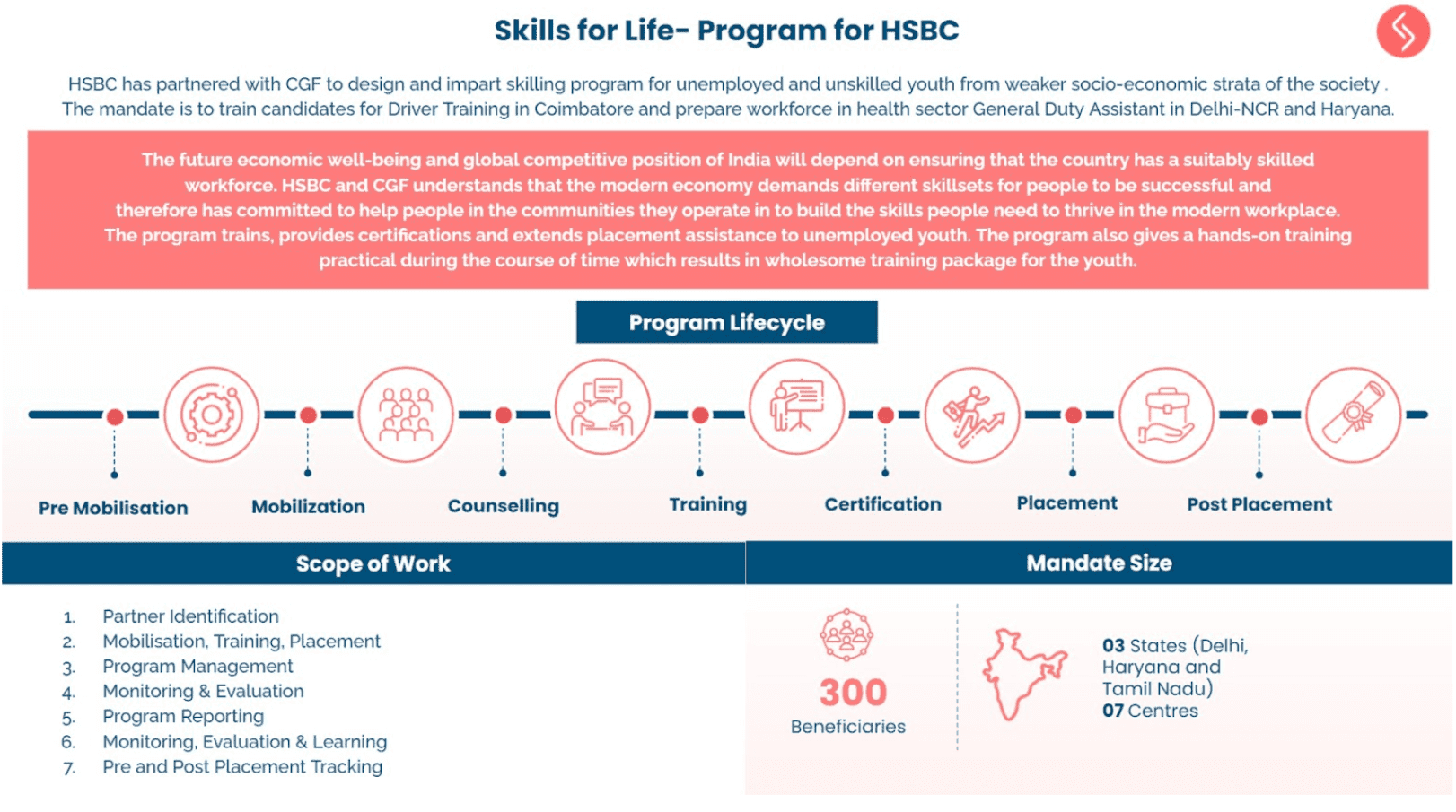
The Need for Partnership: Empowering Women-led Businesses through Collaboration
In this series, we delve on the key lessons from the Samhita -Collective Good Foundation (Samhita-CGF) and Microsoft Project on how to empower women entrepreneurs through digital financial literacy and build a stronger framework for the second iteration.
Women Entrepreneurship: The Indian Landscape
The COVID-19 pandemic had long-lasting devastating effects on the Indian economy, especially when more than 75% of small-scale livelihood families, who were into jobs like farming, construction and owned shops/stalls lost their ability to earn their daily wage income. But it also inevitably encouraged a new wave of women entrepreneurship, as the women, who were traditionally homemakers, realised that they could utilise their basic skills to make masks and other products and generate money, and decided to take on the mantle to run their households for the sake of survival through those tough times.
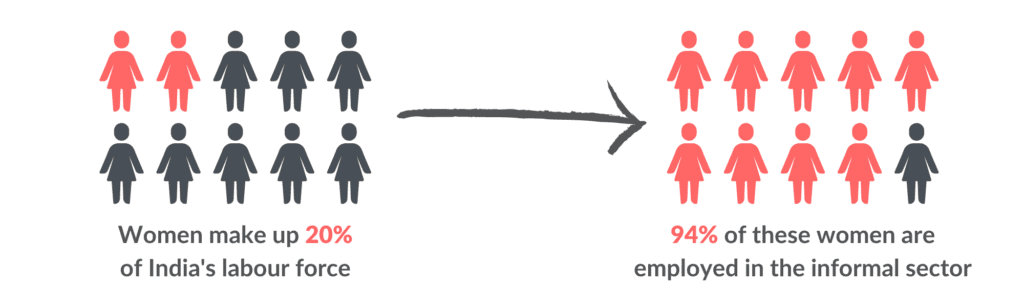
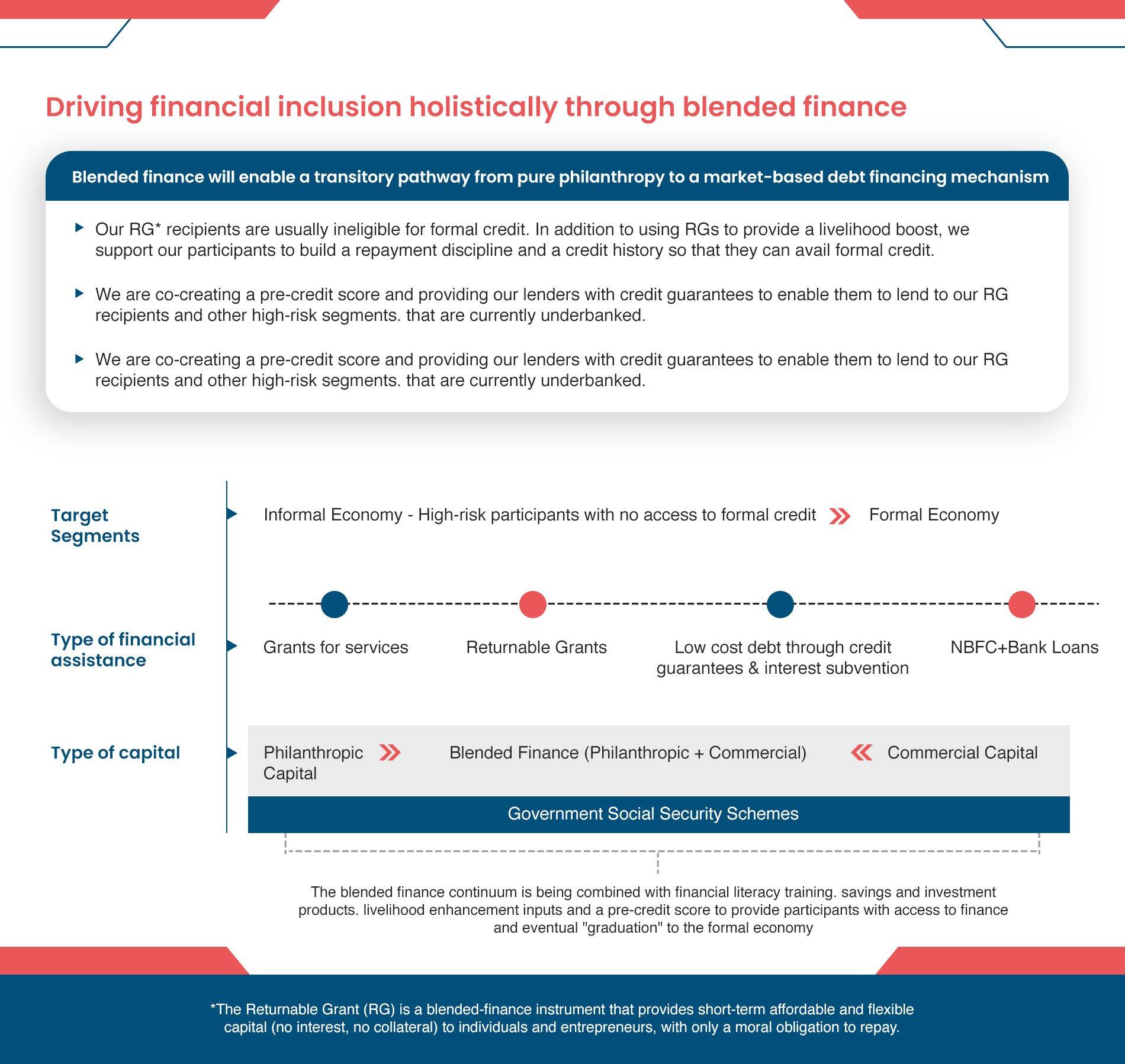
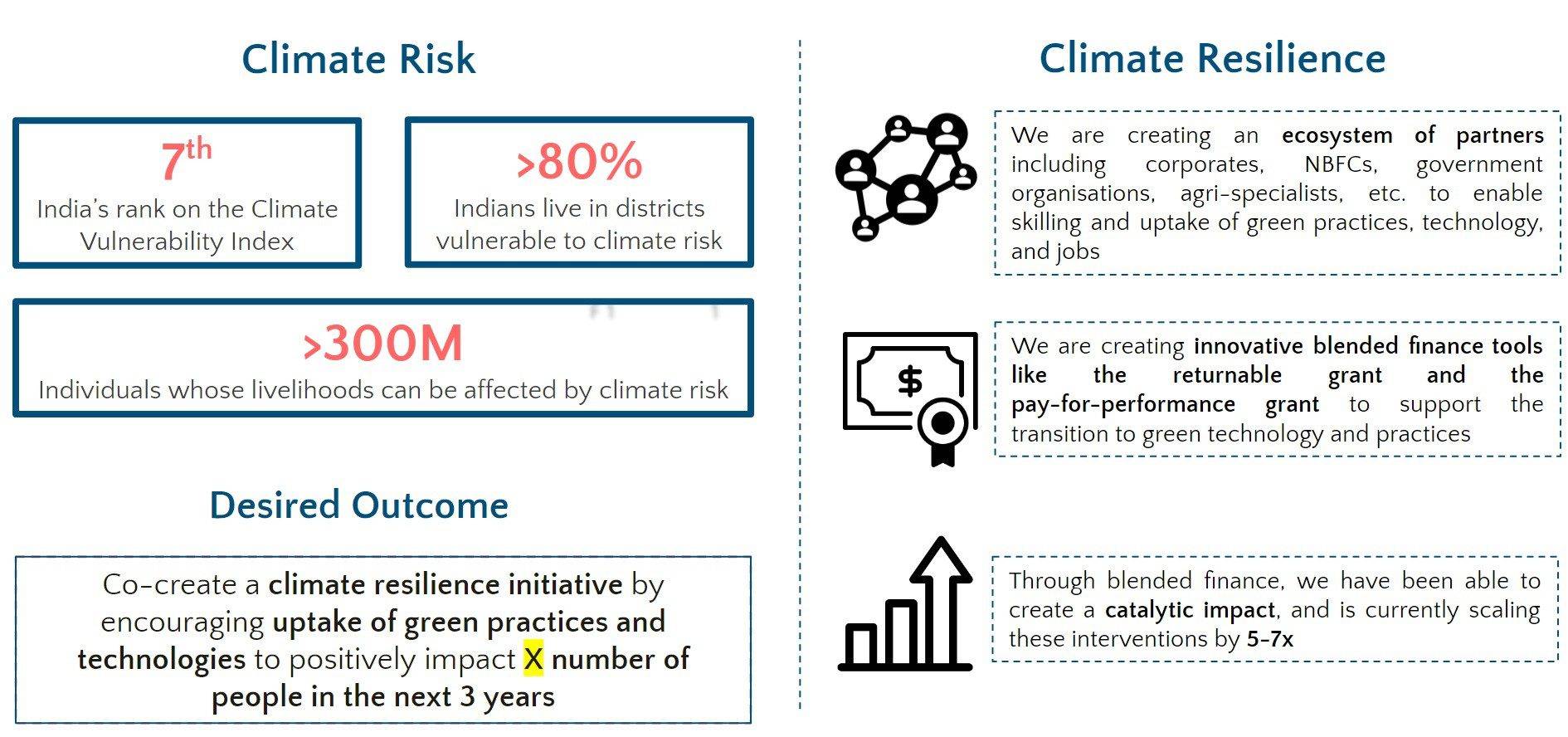
This wave of change quickly transformed women entrepreneurship into a fast-growing sector, and as of 2022, there are more than 13.5 million women-led enterprises in India. But they still attribute to only 20% of the total entrepreneurship in India. There is much more that needs to be done, and that can happen with the help of digital and financial inclusion. Financial inclusion can be considered the basis for enhancing the economic growth and empowerment of a particular country, and is a core need when thinking of establishing any entrepreneurship. This is even more imperative for women, as they lack the financial independence that is naturally granted to men in a patriarchal society. This is in different forms as outlined below:
BARRIERS TO ENTRY
- Socioeconomic and Cultural Barriers: There are many women who still end up handling a second shift model, where they are expected to handle both their businesses and homes simultaneously. 63% of women prefer to work from home for the same reason. This restricts their ability to expand their businesses, as they are not able to give in more time to establish it.
- Lack of Access to Funding: Women entrepreneurs usually tend to depend on immediate family, friends and relatives for financial support to start up and establish their business. Due to lack of financial literacy, many women do not even know how to be able to handle their own bank accounts. As a result, even as of 2022, even with 85% women who have bank accounts, there is a 37% gap in funding for women enterprises.
- Low level of awareness of government schemes: There are a variety of social security schemes provided by the Government of India like financial inclusion, insurance and direct benefit transfers (DBTs)which help to safeguard the future of Indian citizens, irrespective of gender, age, religion or class. However, a majority of women are not aware about them because it is not a topic that comes up in general discussions with other women.
All of these factors play a significant role in determining how women-led businesses are able to flourish in the Indian market.
EMPOWERING WOMEN
Financial and Digital Empowerment of Small Women-Led Businesses
In order to recognise the need to bridge the gap between women entrepreneurs and digital financial mechanisms, Microsoft decided to empower 5000 women through their pan-India scale-up project with Samhita-CGF. These interventions included:
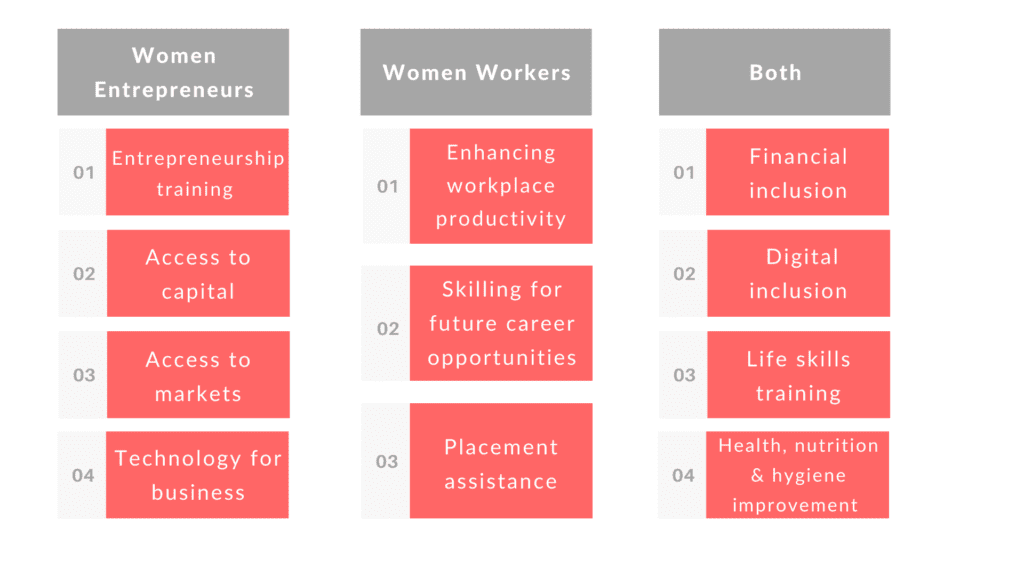
- Provision of access to government schemes and services: The women entrepreneurs were made aware about the schemes provided by the Government of India, broadly covering financial inclusion, insurance and direct benefit transfers (DBTs). They were educated about eligibility criteria, and were provided with hand-holding support in procuring the scheme related documents, and the post-application process.
- Advanced entrepreneurship training: The women were trained on the MeraBills digital bookkeeping app, on topics like retaining a bank account, cash flow management and how to use the digital banking services. Additionally, they were taught financial planning. The entrepreneurs were also provided training the marketplaces to sell their products.
- Mentoring and capacity building to help other members with their existing skill sets: The entrepreneurs who were provided with the advanced training were also moulded to become mentors to the other women in the cohort.
- Enabling credit for their respective businesses: Samhita-CGF got in touch with the banks and non-banking financial companies to create a criterion for the beneficiaries to be connected to the right financial schemes that suit their business. The information included the process of loan disbursement, and how they can return the money in the signed period of time.
PARTNERSHIP FOR STRONGER IMPACT
One of the core reasons why partnerships like these are needed is because each firm has their own expertise, which can be utilised to help those that need it the most. For instance, Microsoft has access to the most innovative technological services available, while Samhita-CGF, through its REVIVE program has an understanding and expertise on financial inclusion. They also give businesses a chance to expand their particular customer base which makes it easier to reach out to more beneficiaries.
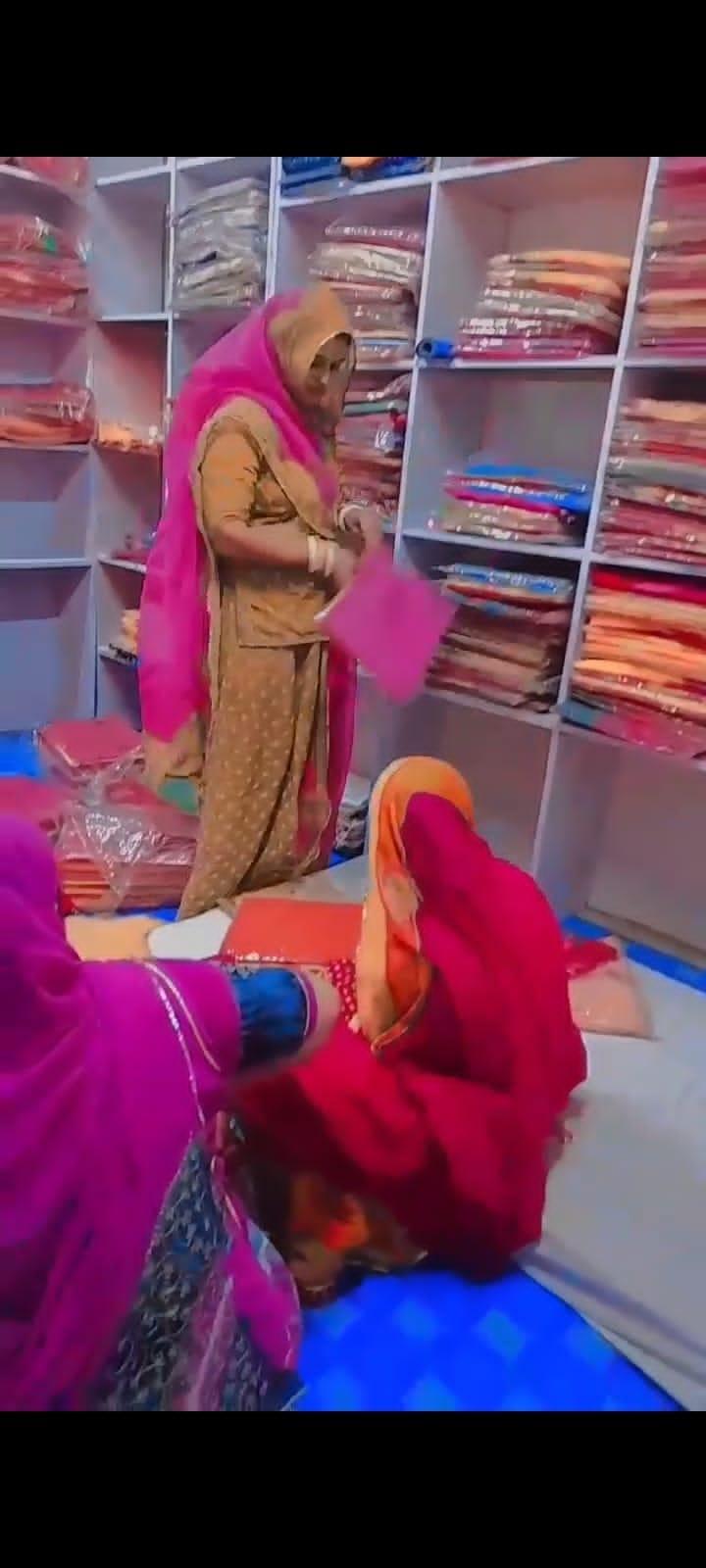
Stitching Her Business with Digital Empowerment: Meenakshi from Barmer
“Now I’m able to take money from my creditor and keep
monthly accounts of my deposits.”


Meenakshi, a 26-year-old resident of Barmer in Rajasthan has always had a strong desire to contribute to her family’s income through her tailoring business. However, managing the finances was a challenge for her, and she often had to depend on others for assistance. Her lack of familiarity with digital payments and bookkeeping made it difficult for her to transition to the new normal. Fortunately, through the REVIVE Project, Meenakshi was able to acquire the digital financial literacy skills needed to thrive.
Her story is a testament to the power of digital financial literacy in empowering women entrepreneurs. Here’s how she did it:
Meenakshi was introduced to the REVIVE Project through Pappu Kanwar, a master trainer from Barmer. She was taught how to operate the phone, use online banking, and send money using UPI. Additionally, Meenakshi was introduced to a digital bookkeeping app called MeraBills, which made it easy for her to keep track of her finances. In addition to reminders, financial reports, and budgeting, she no longer requires assistance with her finances and is independently operating her business.
Just like Meenakshi, there are several other women micro-entrepreneurs that are being connected to the digital world through skill building.


FINDINGS & WAY FORWARD/ ISSUES TO CONSIDER
Some of the considerations for the future could be as follows:
- Enabling online training via mobile phone: Women who participate in such cohorts usually come from a low-income background, hence have to delve into multiple odd jobs in order to support their families’ livelihoods. Enabling online training will allow more women to be able to participate at their convenience, and hence gain digital and financial literacy skills.
- Having a women-only training: This might prove to be effective in ensuring dissemination of learnings. Additionally, personalising the experience with one-on-one sessions, will help the women to develop more trust in the process and work harder on incorporating digital and financial literacy into their livelihoods.
- Provision of data connectivity: Teaching skills is effective only when the women will be able to practise and use the MeraBills digital bookkeeping app in their shops and neighbourhoods too. Hence, the provision of adequate data connectivity in common service centres, panchayat buildings should also be included as part of the programmes.
- Promoting more diverse learning: Curriculum content is better understood when it is supplemented with stories, videos and activity-based learning. The trainers can be equipped and encouraged to deliver their complex ideas in a simpler manner for the women to be able to better retain the information in the long-term.
- Associating the women with unique identification to track their progress: Women in these cohorts usually use their family’s phone numbers to register and implement the program. Creating a unique id will help to identify them as individuals, and monitor their individual areas of improvement and growth.
- Determining an effective pay-for performance process: On achieving a particular milestone, the women were paid ₹400 to encourage them. However, money can often be seen as charity and/or insufficient for the particular need. A change in amount and more clarity on the rationale to the beneficiaries will help to make the process more efficient.
The Samhita-CGF- Microsoft program has been instrumental in changing the lives of more than 5000 women entrepreneurs so far, and the second iteration will help to take this partnership forward to benefit many more women. It is inspiring to see stories of resilience like Meenakshi, and it is our hope that many such women are able to utilise the digital book-keeping and capacity building skills and tools to further advance their businesses and live a life of dignity.
This article was editorialised by Ayushi Bhatnagar and Tanvi Deshmukh