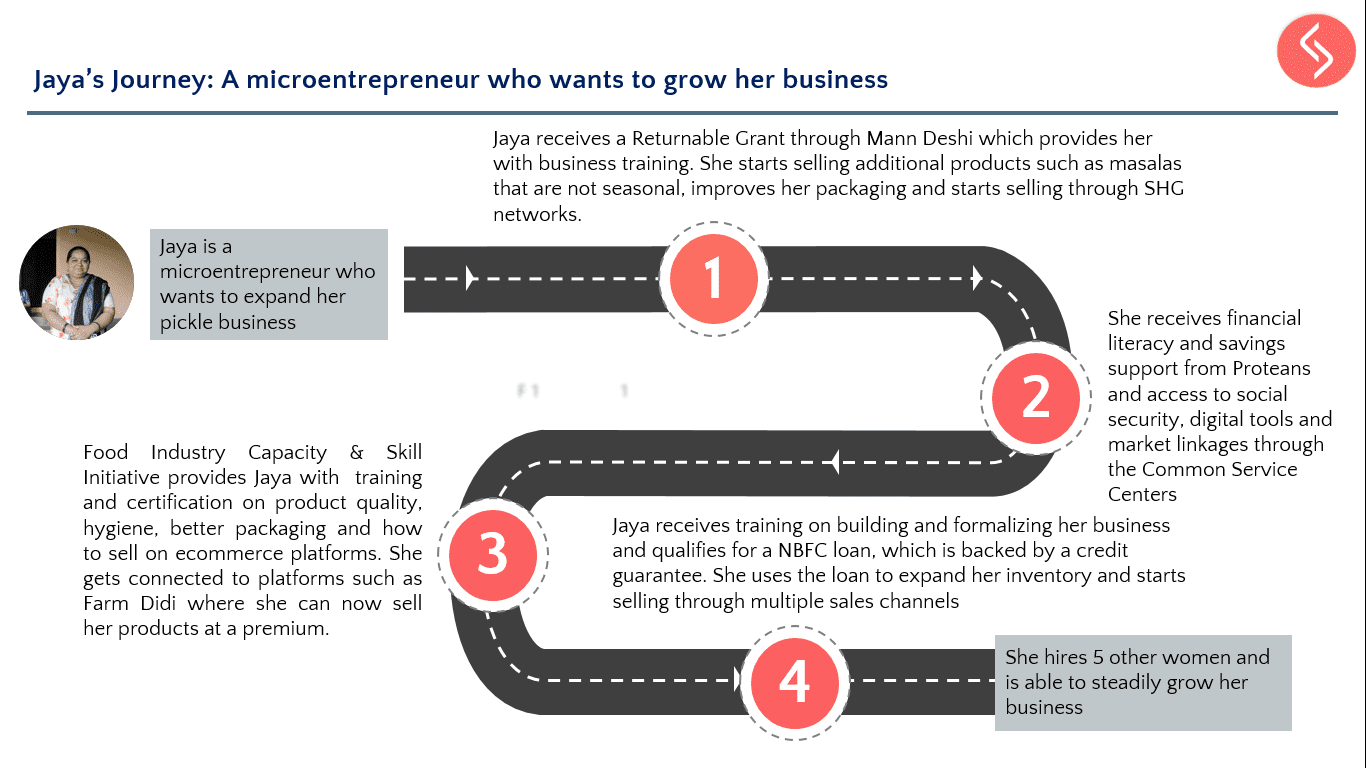
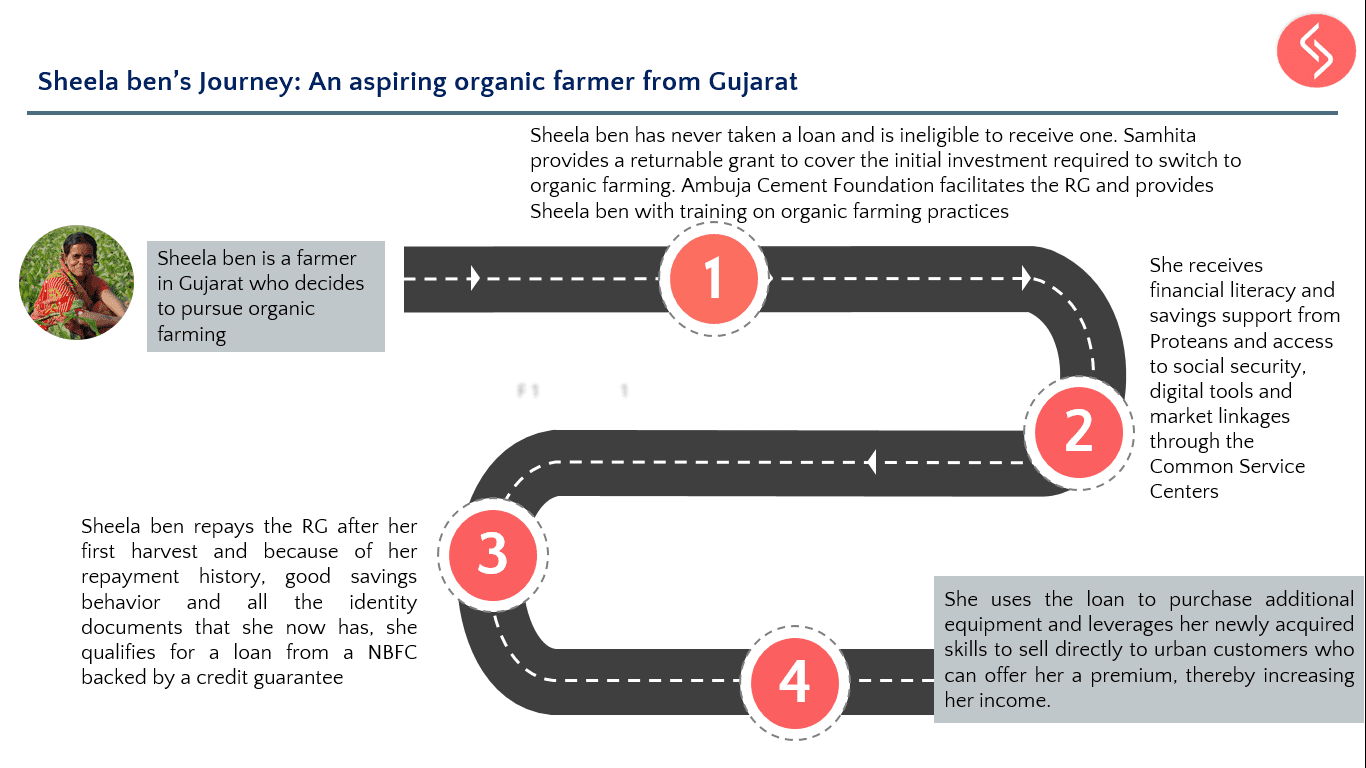
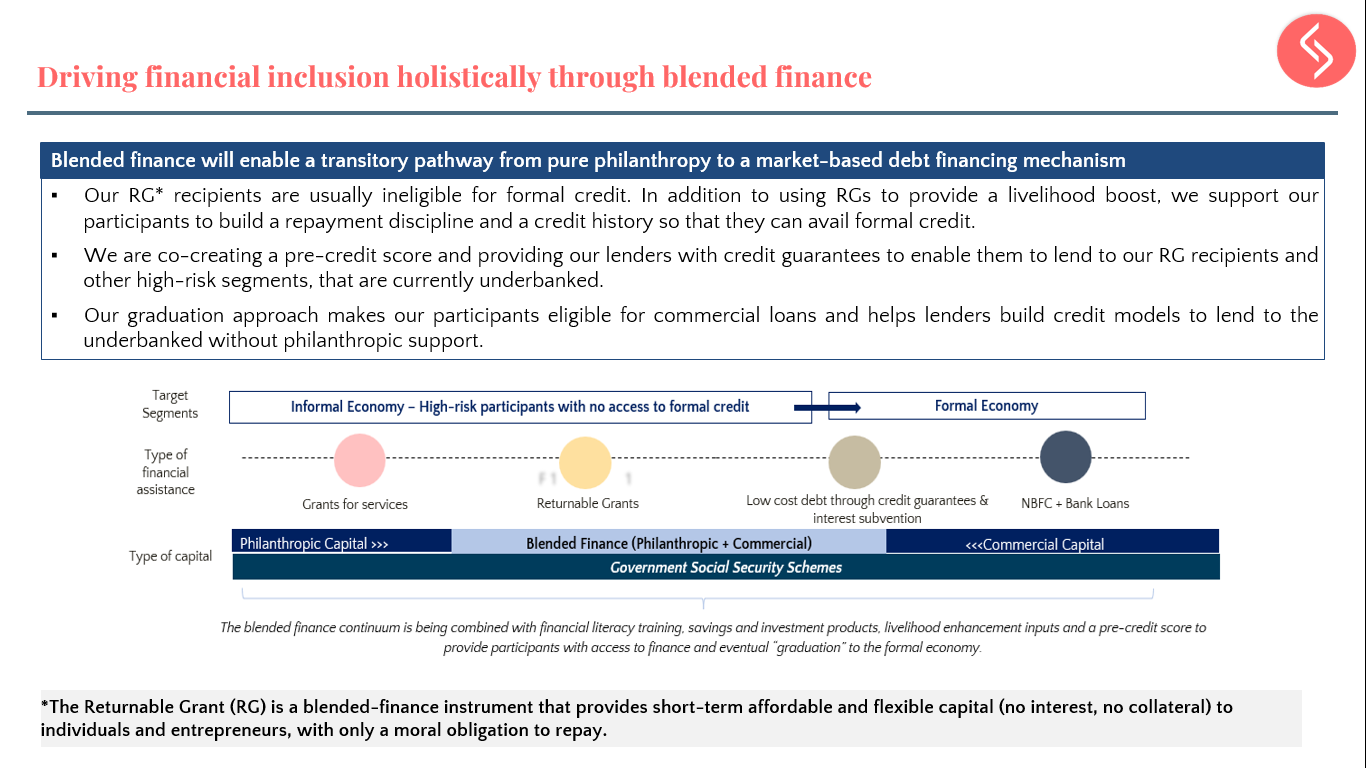
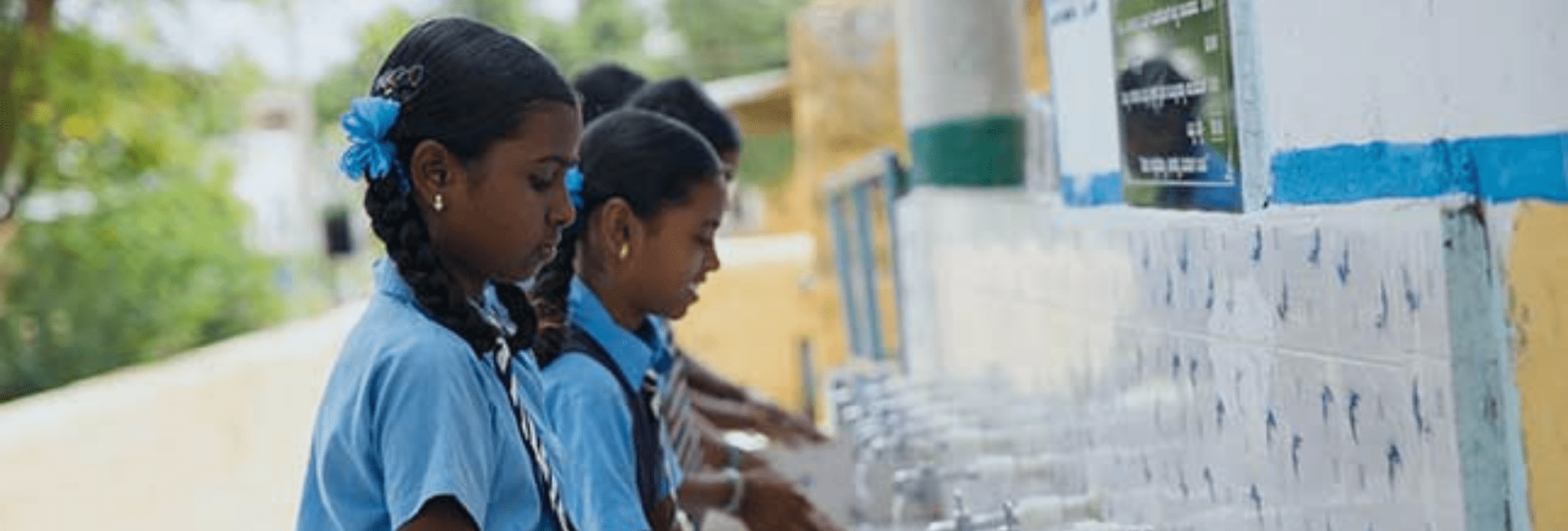1. What CSR programs do you currently focus on in sanitation and the Swachh Bharat mission? How does this align with Reckitt Benckiser’s broader sustainability approach?
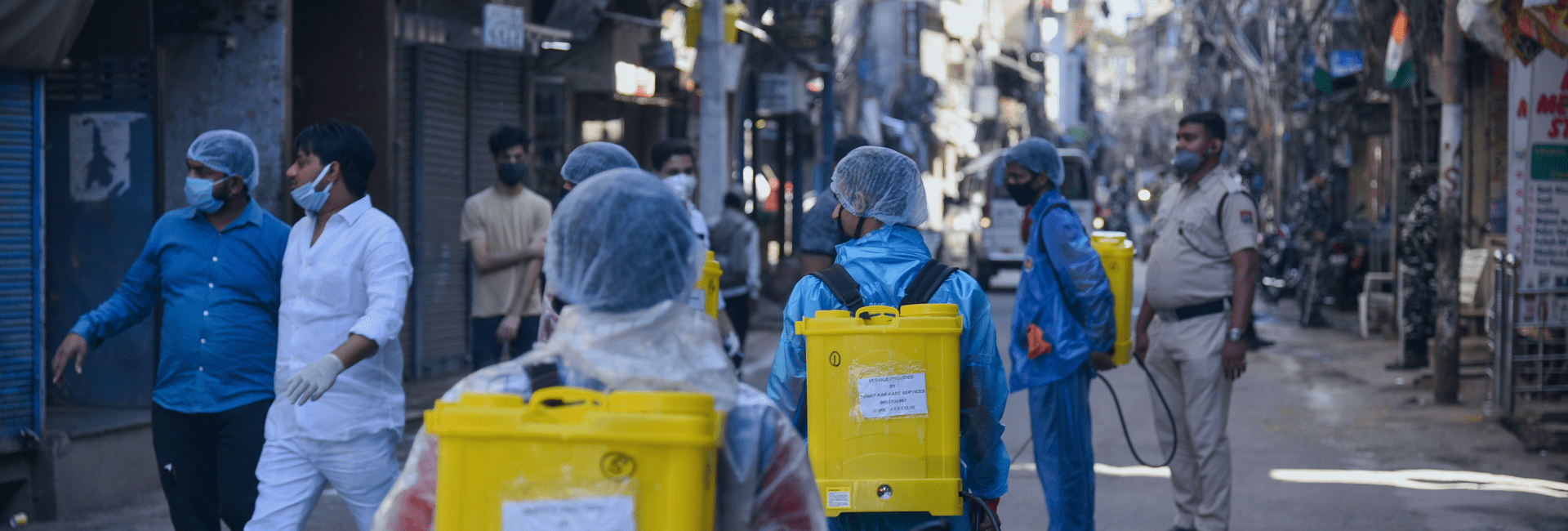
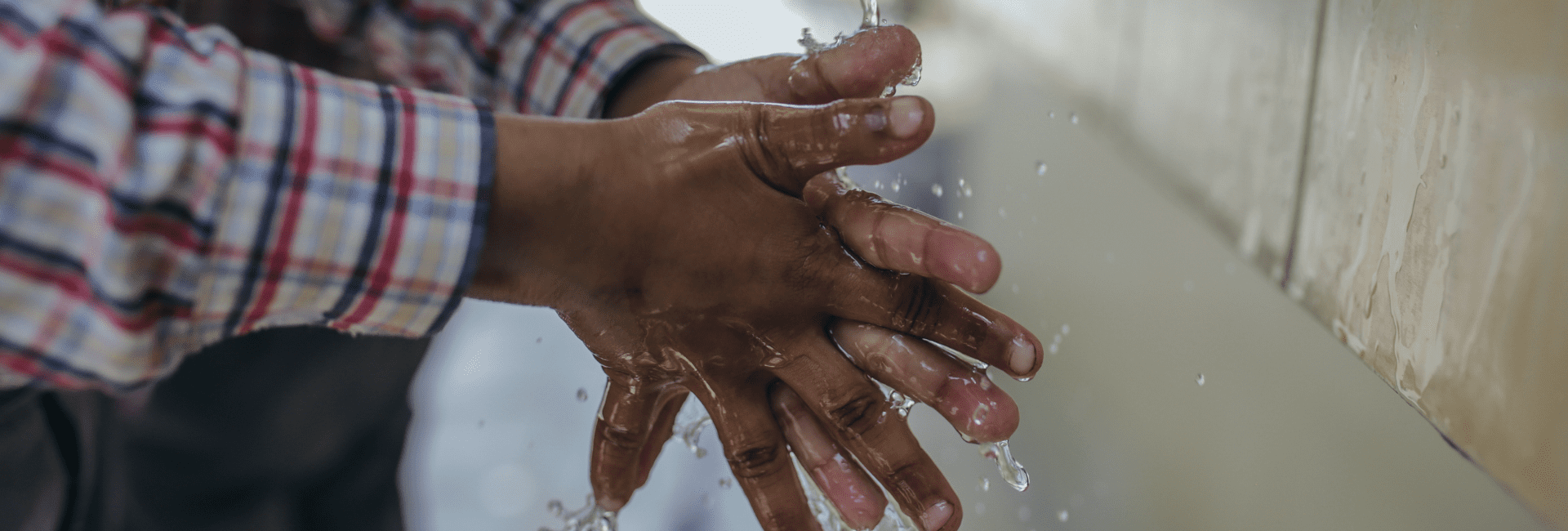
We have a broad responsibility towards Banega Swachh India (BSI). [RB’s ambitious program to address the sanitation and hygiene crisis in India] We work under 4 pillars. The first pillar is behaviour change communication, the second is mass reach, the third pillar is product access and fourth is infrastructure creation and maintenance. We give maximum weight to work around behaviour change communication because we find without BCC infrastructure created will remain only structures that will never be used. So our work is focused around the determinants of behaviour change. We are trying to understand through our work and processes why behaviours are such and what triggers non-behaviours into behaviours.“We give maximum weight to work around behaviour change communication because we find that without BCC infrastructure created…will never be used”
2. Can you tell us about some activities that you have conducted in the area of behaviour change communication?
Under Banega Swachh India (BSI) we are developing school modules for very young children at the foundation stage which include early-learning goals like personal social and emotional development, knowledge and understanding, physical development. Typically what happens is that some hand washing programs are conducted for a session or two. They aren’t regular sessions, just awareness programs. We are trying introduce a program where there will be modules in place for school children, student work books, activity based learning kits and a school curriculum for the teachers amongst other things, so that there is a regularity in the messages that are disseminated. We don’t only work on one aspect which is only hygiene or hand washing. We have elaborate modules that range from personal hygiene to hygiene at home, hygiene at school, hygiene during illness, hygiene in neighbourhoods etc. We are making strides at various levels and building a curriculum to implement good hygiene. In the coming months we will roll out a program with some very worthy partners that have been working with us since the launch of our BSI campaign, which is the Banega Swachh India campaign.
Do you work with other communities as well?
We are starting with schools, but yes we do intend to work with natural leaders and community based leaders. We are also thinking about using a platform to create an enabling environment for the Banega Swachh India campaign to leads us towards the goal of the Swachh Bharat mission. We are currently in dialogue with certain organizations about this.
3. Do you think that organizations are interpreting the Swachh Bharat campaign to mean “build toilets?” There are other aspects of WASH that are not receiving as much attention, why do you think this is so?
I feel that there are various partners so if someone is constructing toilets, it’s a very big part of the mission. To invest in creation of the infrastructure, a lot of capital is involved. But yes, we should leverage resources that everyone has – corporates, private foundations, international organisations, all have resources and it’s important to leverage these to shape the market. One part is construction of toilets which is very important, but along with that, companies can come up with various things. Companies have brands and conduct campaigns and so we have experience in this area. We can do something to motivate people like bringing like-minded people together so that everyone contributes. It should not be a standalone thing – there needs to be a spirit of partnership on mutually agreed principles so that people work together and achieve the goal of making India open-defecation free.
4. What are the main issues that you think need intervention in sanitation and how does RB approach these issues?
What’s important here is to work as a consortium rather than alone, because organizations have different skill sets and different strengths, so if everyone comes together there’s a good chance things will happen. To take the example of Samhita and how you bring in multiple stakeholders for an issue – if we do that then we will know what TCS is doing, how someone else is contributing etc. No organization or company can do this alone, we need to fit in with the overall vision of Swachh Bharat. We are currently exploring the best ways to do this.
5. At the Chicago Booth event, you mentioned an innovative approach that RB is implementing, can you tell us a little bit more about that?
Our work is of 2 kinds. One is hardcore execution on the field through intervention partners. We work on bringing partners together and we also bring some global people together so that the best can be achieved. Our second approach is working on something which is more on the policy level. Here we’re looking at how all this work can be integrated into the larger framework of sanitation.
6. What do see as the major obstacles or challenges to having a Swachh Bharat? What challenges has RB faced?
Let’s call it learnings, not challenges. We see opportunities for where we can do better, not just the challenges. I think we need to have more partnerships and more aligned thinking. It’s very important to have design thinking. We are continuously working on that – improving our design thinking.
7. What do you see as the key development issues in India? What is the role that companies can play?
You see, health, hygiene, sanitation they all go hand in hand. There are various things that need our urgent attention. You must know that India has committed to the MDGs. The MDGs talk about the latest figures for under 5 mortality and morbidity arising out of diarrhoea. That’s one of the things which is very important. A lot of theories state that this is an unexplored space where companies can come forward to contribute. There are only a few foundations working in this area.
I also see that very simple things like hand-washing can reduce diarrhoea and pneumonia mortality and morbidity rates using very simple tools.
There are 3 aspects on which define your CSR strategy – one is the company’s mission the other is sustainability goal of the company and the third is seeing if there is a match between the two. I would also like to say that without partnerships no one can achieve anything. This is the time to work together to achieve Swatch Bharat Mission and make India Open Defecation Free.